Breast cancer and female genital tract cancers (such as cervical, ovarian, uterine/endometrial, and vaginal cancers) are among the most common cancers affecting women worldwide. These cancers occur when abnormal cells grow uncontrollably in the breast tissue or the reproductive organs of the female genital tract.
Breast Cancer
Breast cancer usually begins in the ducts or lobules of the breast. It may present as a lump, nipple discharge, or changes in breast shape/skin. Early detection through regular self-examination and screening (like mammography) significantly improves treatment success.
Female Genital Tract Cancers
- Cervical Cancer – often linked to HPV infection, preventable with vaccination and early Pap smear screening.
- Ovarian Cancer – known as the "silent killer" due to vague early symptoms.
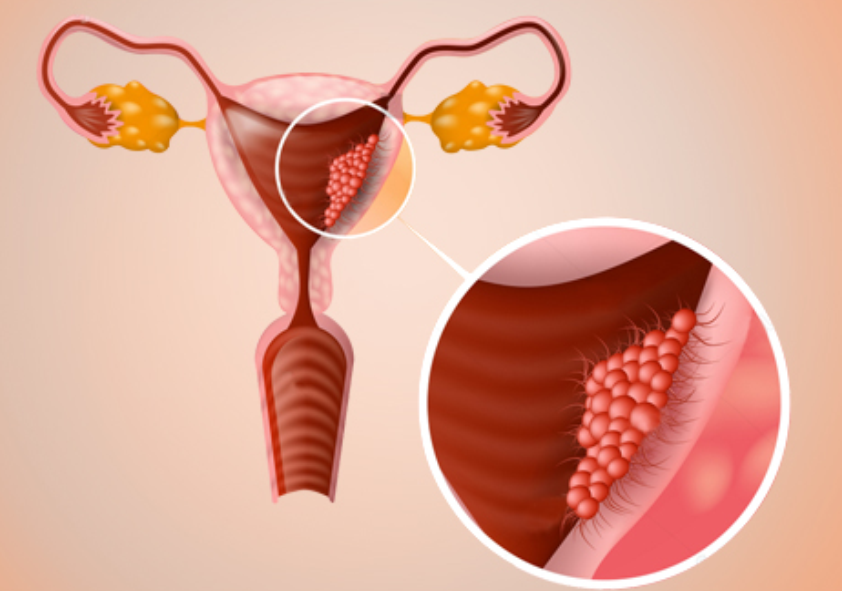
- Uterine/Endometrial Cancer – typically presents with abnormal bleeding.
- Vaginal/Vulvar Cancer – less common but important to diagnose early.
Treatment Options
Treatment depends on the type and stage of cancer, patient’s age, and overall health. Common options include:
- Surgery – Removal of the tumor or affected organ (lumpectomy, mastectomy, hysterectomy, oophorectomy).
- Radiation Therapy – Targets cancer cells with high-energy rays.
- Chemotherapy – Uses drugs to destroy cancer cells or stop growth.
- Hormone Therapy – Useful in hormone-sensitive breast and uterine cancers.
- Targeted Therapy & Immunotherapy – Advanced treatments that attack cancer cells with fewer side effects.
Benefits of Treatment:
- Improved survival – Early and effective treatment increases cure rates.
- Symptom relief – Reduces pain, bleeding, or discomfort caused by tumors.
- Better quality of life – Many women return to normal activities post-treatment.
- Preventive aspect – Early surgery or treatment can stop cancer from spreading.
Risks of Treatment:
- Side effects – Chemotherapy and radiation may cause fatigue, nausea, hair loss, or skin irritation.
- Surgical risks – Infection, bleeding, or complications from anesthesia.
- Fertility concerns – Some treatments may affect the ability to conceive.
- Emotional impact – Body image changes, anxiety, or depression are common.